quality is all pervasive, it is used when qualifying characteristics of products, services, processes, materials & even people. You can find high Quality, Good Quality, Poor Quality, Great Quality and more. There are Quality Actors, Quality Sports persons, Quality engineers and Quality doctors. We also have Quality Stocks, Quality products, Quality Services, Quality Materials and Quality processes.
Quality is omnipresent. Saying a thing has no Quality does not imply a complete absence of Quality. On a Quantitative scale it would only tend towards Zero. If we look at the origins of the word, it is used to Qualify the characteristic of a thing or person.
The dictionaries provide multiple meanings such as
a) A distinctive attribute or characteristic possessed by someone or something
b) The standard of something as measured against other things of a similar kind;
c) The degree of excellence of something.
In a business context, ISO, ASQ and similar standards, industry communities, experts all have provided there views (See Wikipedia for a list of definitions)
Who is a Quality Professional ?
Being all pervasive as above, what does it mean to professionals who have the term Quality attached to their Roles & Designations ? (I.e. Quality Engineer, Quality Auditor, Quality Consultant, Quality Manager) what is expected of a Quality professional?
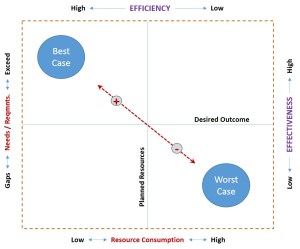
Quality professionals are conscience keepers. All of their thinking & Actions are derived from two overarching Questions. “Are we doing the right things? Are we doing the things Right?” Quality professionals strive to enable & ensure Effective execution of Planned Strategies.
All of the tools, methods, Models, Frameworks, Practices, Standards and more, available at their disposal, supports them in the endeavor.
Lean (Maximize Value by eliminating waste), Six Sigma (Reduce Variation, Improve Stability & Capability), ISO, CMMI, TQM, BPM, Project Management, Risk based thinking, Problem Solving methods, are all various weapons in the Quality professionals Arsenal to help be effective conscience keepers